class: center, middle, inverse, title-slide # 久期 ## Duration ### 吴燕丰 ### 江西财大 金融学院 ### 2020/04/17 --- background-image: url(images/JXUFE.png) --- ### 债券现金流(cash flows)与久期(duration) .center[  ] <br><br> - bond: 债券; - time(years) to maturity: 到到期日时间 --- ### 债券久期(Duration) **定义**:现金支付.red[时刻]的加权平均,权重为每笔现金现值占债券价格比重。 `\begin{align} D \text{ (久期) } &= \sum_{t=1}^T \stackrel{\text{现值占比}}{\overbrace{W_t}} \times \stackrel{\text{支付时刻}}{\overbrace{t}}\\ W_t \text{ (权重) } &= \frac{CF_t/(1+r)^t}{P} = \frac{PV_t(\text{t期现值})}{P(\text{债券价格})} \end{align}` 其中, - `\(CF_t\)` :债券第t期支付现金 - `\(P\)` :债券市场价格 - `\(r\)` :市场价格 `\(P\)` 对应到期收益率 $$ \text{ 提示:}P = \sum_{t=1}^T\frac{CF_t}{(1+r)^t}, \quad \text{ 其中 }\frac{CF_t}{(1+r)^t} \text{ 为第t期现金现值。 } $$ --- ### 久期作为平衡点的解释 设平衡点为 `\(t_{bp}\)`,则平衡点应满足的式子: `$$PV(1)\times(t_{bp}-1) + PV(2)\times(t_{bp}-2) = PV(3)\times(3-t_{bp})$$` `\begin{align} &PV(1)\times t_{bp} + PV(2)\times t_{bp} - PV(1)\times 1 - PV(2)\times 2 \\ &= PV(3)\times 3 - PV(3)\times t_{bp}\\ &PV(1)\times t_{bp} + PV(2)\times t_{bp} + PV(3)\times t_{bp}\\ &= PV(1)\times 1 + PV(2)\times 2 + PV(3)\times 3 \end{align}` `\begin{align} t_{bp} &= \frac{PV(1)\times 1 + PV(2)\times 2 + PV(3)\times 3}{PV(1)+PV(2)+PV(3)}\\ t_{bp} &= \frac{PV(1)\times 1 + PV(2)\times 2 + PV(3)\times 3}{P}\\ &= \sum_{t=1}^3\frac{PV(t)}{P}\times t\\ &= D \end{align}` --- ### 案例图示 .center[  ] --- ### 案例计算 <br><br> `\begin{align} P &= \frac{80}{(1+10\%)} &+& \frac{80}{(1+10\%)^2} &+& \frac{80+1000}{(1+10\%)^3}\\ &= 72.73\text{ (PV(1)) } &+& 66.12\text{ (PV(2)) } &+& 811.40\text{ (PV(3)) } \\ &= 950.25 & & & &\\ & & & & &\\ & & & & &\\ D &=\frac{72.73\text{ (PV(1)) }}{950.25\text{ (P) }}\times 1 &+&\frac{66.12\text{ (PV(2)) }}{950.25\text{ (P) }}\times 2 &+&\frac{811.40\text{ (PV(3)) }}{950.25\text{ (P) }}\times 3 \\ &= 7.65\%\times 1 &+&6.96\%\times 2 &+&85.39\%\times 3 \\ &= 2.78 \text{(年)} & & & & \end{align}` --- ### 零息债券的久期 **零息债券**(zero-coupon bond)久期 = 剩余期限 .center[  ] --- **债券期限越长,久期越长。** .center[  ] --- .pull-left-80[  ] .pull-right-20[ <br><br><br><br><br><br> 息票率越低,久期越长 ] ??? https://static.seekingalpha.com/uploads/2015/4/22/saupload_3144.jpg --- .pull-left-80[  ] .pull-right-20[ <br><br><br><br><br><br> 息票率越低,久期越长 ] --- ### 久期的特征 .pull-left-70[ <!-- --> ] -- .pull-right-30[ <br><br> 久期特征: - 零息债券:<br> .red[久期 = 期限] - .green[期限越长,久期越长] ] --- ### 久期特征 .pull-left-70[ <!-- --> ] .pull-right-30[ <br><br> 久期特征: - 息票率越高,久期越短 ] --- ### 久期的特征 .pull-left-70[ <!-- --> ] -- .pull-right-30[ <br><br> 久期特征: - 严重折价债券(息票率3% << YTM 15%):.blue[久期先增后减] ] --- ### 久期的特征 .pull-left-70[ 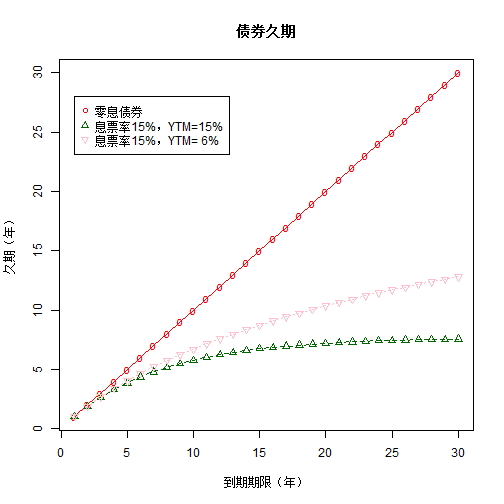<!-- --> ] -- .pull-right-30[ <br><br> 久期特征: - 到期收益率越大,久期越短。 ] --- ### 久期特征小结 久期的一些特征: 1. 每笔现金支付时间,关于其现值占比的加权平均 2. **零息债券**久期 = 期限 3. **附息债券**久期 < 期限: - 期限越长,久期越长 - 期限越长,增幅递减 - 严重折价债券,久期先曾后减 4. 到期收益率越高,久期越短 5. 息票率越高,久期越短 --- ### 久期与债券价格变化关系 `\begin{align} \frac{dp}{P}(\text{债券价格变化%}) &= -\frac{D}{1+y}(\text{调整久期})\times dy(\text{利率变化})\\ \frac{\Delta p}{P}(\text{债券价格变化%}) &\approx -\frac{D}{1+y}(\text{调整久期})\times \Delta y(\text{利率变化}) \end{align}` 注意: - 债券价格**相对变化量**,以%形式表示 - 利率**绝对变化量**,但其本身也以%表示 -- 修正久期与债券价格变化关系: **修正久期越大,债券价格对利率变化越敏感** --- ### 久期与债券价格变化的关系 债券价格公式: `\begin{align} P &= \sum_{t=1}^T\frac{M\times r}{(1+y)^t} + \frac{M}{(1+y)^T} = \sum_{t=1}^T\frac{CF_t}{(1+y)^t} = \sum_{t=1}^T PV_t(\text{第t期现值}) \end{align}` -- 债券价格关于到期收益率的变化: .pull-left[ `\begin{align} \frac{dP}{dy} &= \sum_{t=1}^T\left[\frac{CF_t}{(1+y)^{t+1}}\times (-t)\right]\\ &= -\frac{1}{1+y}\times\sum_{t=1}^T\left[\frac{CF_t}{(1+y)^{t}}\times t\right]\\ &= -\frac{1}{1+y}\times\sum_{t=1}^T\left[ PV_t \times t \right] \end{align}` ] .pull-right[ `\begin{align} \frac{dp}{dy}/P &= -\frac{1}{1+y}\times\sum_{t=1}^{T}\frac{PV_t}{P}\times t \\ &=-\frac{1}{1+y}\times D(\text{久期})\\ \frac{dp}{P} &= -\frac{D}{1+y}\times dy \end{align}` ] --- ### 案例 【例子】:假设票面价值为¥1000的债券,期限为20年,每年付息一次,票面利率为3.5%,到期收益率为5%。 问: 1. 该债券的价格是多少元?修正久期是多少年? 2. 到期收益率上升、下降10个基点(+-0.1%),该债券价格变化率的近似值和实际值分别是多少? 3. 到期收益率上升、下降100个基点( +-1%),该债券价格变化率的近似值和实际值分别是多少? --- ### 案例 1 债券价格,修正久期 `\begin{align} P&=\sum_{t=1}^{20}\frac{35}{(1+5\%)^t} +\frac{1000}{(1+5\%)^{20}} =813.07(\text{元})\\ D&=\sum_{t=1}^{20}\frac{CF_t/(1+5\%)^t}{P}\times t = 14.05(\text{年})\\ D_m(\text{调整D})&= \frac{D}{1+5\%} = 13.38(\text{年}) \end{align}` 2 债券价格近似计算 .pull-left[ `\begin{align} \frac{\Delta P}{P} &\approx -D_m\times\Delta y\\ &\approx -13.38\times(±)0.1\%\\ &\approx (∓)1.338\% \end{align}` ] .pull-right[ `\begin{align} \frac{\Delta P}{P} &\approx -D_m\times\Delta y\\ &\approx -13.38\times(±)1\%\\ &\approx (∓)13.38\% \end{align}` ] --- ### 案例 3 债券价格变化理论计算 `\begin{align} \frac{\Delta P}{P} &=\frac{P(y±0.1\%)-P(y)}{P(y)}; & \frac{\Delta P}{P} &=\frac{P(y±1\%)-P(y)}{P(y)} \end{align}` <br><br> 提示:债券价格公式为 $$ P(y) = \sum_{t=1}^{T}\frac{M\times r}{(1+y)^t} +\frac{M}{(1+y)^T} $$ --- 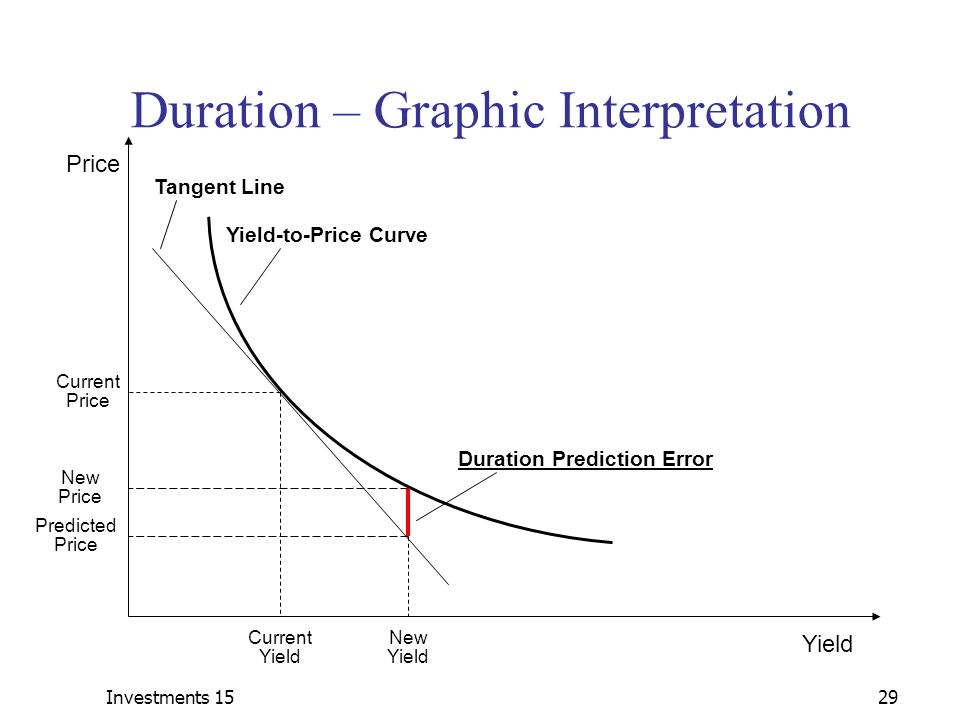 ??? 债券价格关于利率变化近似计算的特征 --- ### 误差特征 .center[ 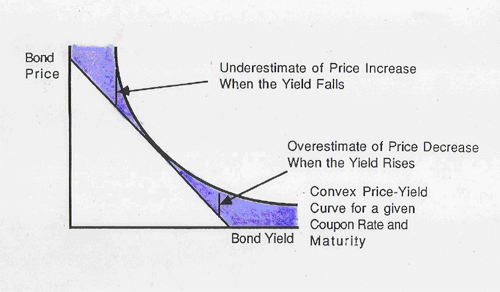 ] --- ### 误差特征 - 利率上升时,高估债券价格下降 - 利率下降时,低估债券价格上升 -- 原因: $$ |\frac{dP(y)}{dy}| \text{ 随着 }y\text{ 的上升,而变小 } $$ $$ \frac{d^2P(y)}{dy^2} > 0 \text{ (凸函数) } $$ -- $$ \frac{d^2P(y)}{dy^2} < 0 \text{ (凹函数) } $$ --- ### 凹凸函数 .pull-left[ 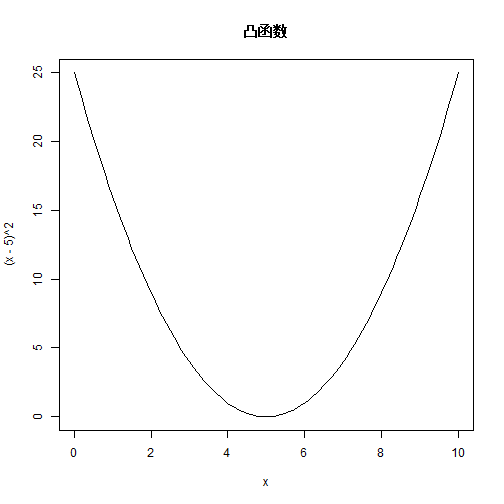<!-- --> ] .pull-right[ <!-- --> ] --- ### 债券价格的二次近似 微分中值定理、泰勒展开 $$ P(y) = P(y_0) + \frac{dP(y_0)}{dy_0}(y-y_0) + \frac{1}{2}\frac{d^2P(y_0)}{dy_0^2}(y-y_0)^2 $$ 提示: - `\(\frac{dP}{dy} <0\)` - `\(\frac{d^2P}{dy^2} >0\)` ---  --- ### 问答